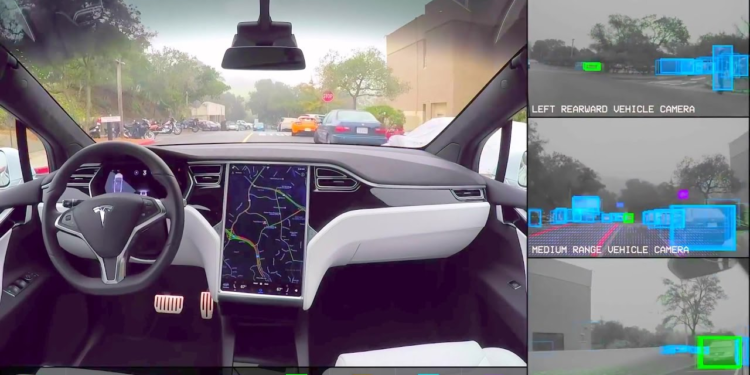
Self-driving vehicle testing is undergoing a significant transformation as new data from California’s Department of Motor Vehicles reveals a sharp decline in autonomous vehicle tests on public roads. In 2024, tech companies recorded only 4.5 million miles of autonomous vehicle testing, a staggering 50% decrease compared to the previous year. This drop highlights a concerning trend, especially in driverless technology testing, which plummeted by 83% from 3.26 million miles in 2023 to just 552,895 miles last year. Key players like Waymo and Cruise have shifted their focus, with Waymo prioritizing commercial operations over extensive testing, while Cruise faced suspension of its permits. As the landscape of driverless technology continues to evolve, these California DMV statistics underscore the growing challenges within the autonomous vehicle testing sector, signaling a need for renewed strategies and innovations.
The landscape of autonomous vehicle trials is shifting dramatically, with recent reports indicating a notable downturn in the frequency of such assessments. The decline in the operational miles logged by driverless technology firms suggests a cautious approach among tech companies as they navigate regulatory hurdles and safety concerns. Companies like Waymo are transitioning from testing to commercializing their services, while others, such as Cruise, have faced significant setbacks. With fewer permits being issued for autonomous and drivered vehicle testing, the industry is consolidating, leaving only a handful of players actively engaged in driverless technology development. As the market adapts to these changes, the future of driverless vehicle trials will depend on effective management of safety standards and innovative advancements.
The Current State of Self-Driving Vehicle Testing in California
As of 2024, self-driving vehicle testing in California has reached a critical juncture, marked by a significant decline in testing miles logged by tech companies. The California DMV has reported a staggering 50% drop in the total test miles, decreasing from 9 million in 2023 to just 4.5 million this year. This downturn is especially pronounced in the area of driverless vehicle testing, which plummeted by 83%, highlighting a troubling trend in the autonomous vehicle sector. The dramatic fall in testing miles raises questions about the viability and safety of driverless technology, prompting discussions among industry experts and stakeholders.
This decline in self-driving vehicle testing can be attributed to several factors, including regulatory scrutiny and evolving safety standards. The DMV’s annual disengagement reports have become a focal point for evaluating the performance of autonomous vehicles, unveiling instances where human intervention was necessary due to technology failures. Such reports complicate the landscape of autonomous vehicle testing, making it challenging to assess the true capabilities of various companies, including industry leaders like Waymo and Cruise.
Factors Contributing to the Decline in Autonomous Vehicle Testing
Several factors have contributed to the marked decrease in autonomous vehicle testing in California. One significant element is the regulatory environment, which has become increasingly stringent in light of safety concerns. The California DMV’s oversight has tightened, with fewer permits being issued for both drivered and driverless testing. In 2024, only one new permit was granted for vehicles with a human driver, a stark contrast to the earlier years when the DMV issued multiple permits to various companies. This shift reflects a growing caution within the regulatory framework, emphasizing the need for rigorous safety protocols.
Additionally, the consolidation of the autonomous vehicle industry has played a role in the decline of active testing. Once populated by numerous startups, the sector has seen many companies withdraw from testing programs or scale back their operations significantly. For instance, major players such as Tesla have ceased logging autonomous miles, while others have faced suspensions or closures. This consolidation has left a handful of companies, like Waymo and Nuro, at the forefront, impacting the competitive landscape of autonomous vehicle technology.
The Role of Waymo and Cruise in Autonomous Testing
Waymo has emerged as a leader in the realm of autonomous vehicle testing, particularly after shifting its focus towards commercial operations in urban areas like San Francisco and Los Angeles. With a robust infrastructure supporting its robotaxi service, Waymo has logged a significant number of miles, though it has reduced its testing activities in favor of commercial deployment. This pivot has allowed Waymo to capitalize on its advancements in driverless technology while navigating the regulatory landscape, which has become more complex over recent years.
In contrast, Cruise, once a prominent player in autonomous vehicle testing, faced challenges that led to the suspension of its permits. After logging 2.6 million test miles in 2023, the company was unable to resume testing in California, leading to doubts about its future in the autonomous vehicle sector. General Motors, Cruise’s parent company, has made strategic decisions that reflect a cautious approach to driverless technology amid declining public confidence and stringent regulatory hurdles. This situation underscores the volatility within the industry and the shifting fortunes of companies engaged in autonomous vehicle testing.
Implications of the Decrease in Driverless Testing
The decline in driverless vehicle testing has serious implications for the future of autonomous technology. With a significant drop in testing miles, the progress toward fully operational self-driving vehicles may be hindered. The reduction in testing could stall innovation and delay the realization of a fully autonomous transportation network. As the industry grapples with safety concerns and regulatory pressures, the public’s perception of driverless technology may also shift, potentially leading to decreased investment and support for future developments.
Furthermore, the dramatic reduction in testing miles raises critical questions about the readiness of autonomous vehicles for widespread deployment. With fewer companies actively testing their technologies, the competition that initially drove innovation in the sector has diminished. This consolidation could result in a slower pace of technological advancement, as fewer players can lead to a lack of diverse approaches and solutions to the challenges faced by autonomous vehicles.
Challenges Faced by Autonomous Vehicle Companies
Companies involved in autonomous vehicle technology face a myriad of challenges that have contributed to the decline in testing. Regulatory hurdles, safety concerns, and public skepticism are just a few of the obstacles that these companies must navigate. The California DMV’s strict oversight and the requirement for comprehensive safety protocols have made it increasingly difficult for new players to enter the market, while established companies struggle to maintain their testing permits amid growing scrutiny.
Additionally, the technological challenges of developing robust driverless systems that can operate safely in diverse environments cannot be overlooked. Instances of disengagement, where human drivers must take control due to system failures, highlight the limitations of current autonomous technologies. These challenges necessitate ongoing research and development, but as funding and resources become scarce, many companies may find it difficult to sustain their operations and drive innovation forward.
The Future of Self-Driving Technology: A Look Ahead
Looking ahead, the future of self-driving technology remains uncertain as the industry grapples with regulatory challenges and public perception issues. With only a few companies actively engaged in testing, the landscape is poised for potential change. Companies like Waymo are focusing on scaling their commercial operations, which may set the tone for the future of autonomous vehicles. However, the decline in testing miles raises concerns about the pace of development and the readiness of these technologies for broader adoption.
Moreover, the ongoing evolution of driverless technology necessitates a collaborative approach among industry stakeholders, regulators, and the public. To foster innovation and regain public trust, companies must prioritize transparency in their testing processes and demonstrate the safety and reliability of their systems. As the autonomous vehicle industry continues to adapt to the current climate, its ability to address these challenges will determine the trajectory of self-driving technology in the coming years.
The Impact of Market Consolidation on Autonomous Vehicle Testing
Market consolidation within the autonomous vehicle sector has altered the dynamics of testing and development. As numerous startups have folded or been acquired, the industry has narrowed down to a select few players. This consolidation has implications for innovation, as fewer companies competing for advancements can lead to stagnation in technology development. The remaining companies, such as Waymo and Nuro, must not only innovate but also demonstrate their capabilities in a landscape where scrutiny is at an all-time high.
Additionally, the concentration of resources among a limited number of companies may lead to a disparity in testing capabilities. With only a handful of firms conducting significant testing, there is a risk that the industry may overlook alternative approaches that could drive advancements in autonomous technology. This could further entrench the dominance of a few key players, limiting the potential for diverse solutions and hindering the overall progress of the self-driving vehicle sector.
Evaluating Safety Standards in Autonomous Vehicle Testing
Safety standards in autonomous vehicle testing are of paramount importance as the industry seeks to establish reliable and trustworthy technology. The California DMV’s annual disengagement reports serve as critical tools for assessing the safety and performance of autonomous vehicles. However, the varying standards and practices among different companies complicate the evaluation process. Without a unified framework for assessing safety, it becomes challenging to compare the efficacy of different autonomous systems and to determine which technologies are truly ready for public deployment.
As the industry moves forward, establishing standardized safety metrics will be essential. This will not only provide clarity for regulators but also help consumers understand the capabilities and limitations of autonomous vehicles. Companies must commit to transparency in their testing methodologies and share data that can help build a comprehensive understanding of safety in driverless technology. By prioritizing safety and accountability, the autonomous vehicle sector can work towards regaining public confidence and ensuring a successful transition to self-driving technology.
The Role of Investment in Autonomous Vehicle Development
Investment has played a crucial role in the development of autonomous vehicle technology, fueling research and innovation. However, the recent decline in testing and the reduction in the number of active players have raised concerns about future funding. With fewer companies competing for investment, there is a risk that the momentum built over the past few years could be lost. Investors are likely to be more cautious, focusing on companies that demonstrate a clear path to commercial viability and safety in their technologies.
To attract continued investment, companies in the autonomous vehicle sector must showcase their advancements and emphasize their commitment to safety and innovation. Demonstrating successful testing results and a clear regulatory strategy will be key in instilling confidence among investors. As the industry navigates this transitional phase, the ability to secure funding will be vital for companies looking to advance their technologies and compete in a challenging marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the latest California DMV statistics on self-driving vehicle testing for 2024?
According to the latest California DMV statistics for 2024, self-driving vehicle testing logged a total of 4.5 million miles, which represents a 50% decrease from the previous year. This figure includes both autonomous vehicle testing with human safety drivers and driverless technology testing.
How has the decline in driverless technology testing affected companies like Waymo and Cruise?
The decline in driverless technology testing has significantly impacted companies such as Waymo and Cruise. Waymo has pivoted to focus more on commercial robotaxi services rather than extensive testing, while Cruise saw a drastic drop in testing miles from 2.6 million in 2023 to a halt in 2024 following permit suspensions.
What challenges does the self-driving vehicle testing industry face according to the DMV’s disengagement reports?
The self-driving vehicle testing industry faces challenges highlighted in the DMV’s disengagement reports, which document instances where human drivers had to regain control due to technology failures. The inconsistency in reporting standards among companies complicates the assessment of autonomous vehicle technology proficiency.
Why did the number of permits for self-driving vehicle testing decline significantly in recent years?
The number of permits for self-driving vehicle testing has declined due to a consolidation trend within the industry, where fewer companies are willing to invest heavily in autonomous vehicle technology. In 2024, only one new permit was issued, indicating a reduced interest in public road testing.
What are the implications of the 83% drop in driverless testing miles reported by the California DMV?
The 83% drop in driverless testing miles, falling to just 552,895 in 2024, suggests a significant slowdown in the development and deployment of driverless technology. This decline raises concerns about the progress of autonomous vehicle testing and the future of driverless options in the market.
Which companies currently hold permits for self-driving vehicle testing and what types of testing do they conduct?
As of 2024, only 31 companies hold permits for self-driving vehicle testing, with just 11 actively conducting public road testing. Companies like Waymo and Nuro have been granted permits for driverless testing, while Mercedes-Benz has advanced systems allowing hands-free driving.
What does the future hold for self-driving vehicle testing in light of recent trends?
The future of self-driving vehicle testing appears uncertain given the recent trends of declining test miles and permit issuances. With major players like Waymo focusing on commercialization and others like Cruise halting operations, the industry may continue to experience consolidation and reduced competition.
How does Waymo’s strategy differ from other companies in self-driving vehicle testing?
Waymo’s strategy has shifted towards offering commercial robotaxi services rather than focusing solely on extensive self-driving vehicle testing. This contrasts with other companies that may still be heavily engaged in testing phases, reflecting a broader industry trend towards commercialization.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Testing Decline | Self-driving vehicle testing has decreased by 50% in 2024, totaling 4.5 million miles. |
| Driverless Testing Drop | Driverless testing miles fell by 83%, from 3.26 million in 2023 to 552,895 in 2024. |
| Permit Trends | Only 31 companies currently hold permits for testing; only 11 conducted public testing in 2024. |
| Disengagement Reports | DMV reports highlight instances where human drivers had to take control, causing controversy. |
| Market Consolidation | The market has consolidated, with key players like Waymo focusing on commercial operations. |
Summary
Self-driving vehicle testing has faced significant challenges in recent years, particularly in California, where recent data shows a drastic reduction in testing miles and permits. As companies like Waymo and Cruise navigate the complexities of regulations and market demands, the future of autonomous vehicle technology remains uncertain, emphasizing the need for a more competitive landscape in self-driving vehicle testing.